Graphics:Models
By augmenting a sprite with additional information, we can create an object that is ready for placement on the map: a model.
Purpose of Models
A model combines the graphical representation of an object with a physical shape. As explained in the chapter about in-game graphics, sprites are drawn to give a 3-dimensional appearance to the game world. Internally, the engine uses indeed a (simple) 3-dimensional representation for the purpose of collision detection and rendering. The shape of each model is used to build this internal 3D representation and the sprite is used to visualize it on screen.
As such, it is important to understand how sprite and shape fit together, as only precisely built models will ensure a game world where characters won't get stuck or fall through the ground and where objects are rendered without glitches.
Construction of Models
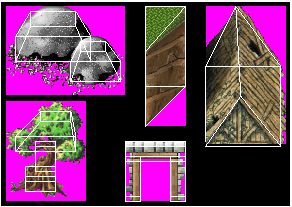
Since the 3D representation will not be visible directly, it does not have to be very detailed. Therefore, the basic shape is a simple cube. It can be deformed to match the actual sprite and, where necessary, multiple cubes can be used to represent more complex sprites.
For non-rectangular sprites, individual corners of the cube can be moved freely in space and even onto each other to make diagonal or triangular shapes. Note however that it is not allowed to make completely flat (i.e. two-dimensional) shapes, as collision detection will not function properly around those. So even floor tiles will have to have a certain height.
To align a sprite with the shapes, an additional offset can be specified. This offset is only 2-dimensional, since from the renderers perspective, depth and height (y and z axis) are the same.
To aid with the construction of models, the modeller tool has been created. There is a tutorial providing step-by-step instructions to its basic functionality and a more detailed reference explaining all of its features.