Widget Set: Difference between revisions
m →Widgets |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
=Possible Changes= | =Possible Changes= | ||
*It may not be necessary for base and widget to be to separate classes. The only reason is if there is a need to differentiate between widget and layout objects. | *It may not be necessary for base and widget to be to separate classes. The only reason is if there is a need to differentiate between widget and layout objects. | ||
=Screen Shot of Current Work= | |||
Beware, programmer art shown: | |||
[[Image:Guisshot.png]] | |||
Shown here are two option boxes, three labels, three textboxes, and two buttons. These are contained by a hierarchy of three layout objects. | |||
Revision as of 18:37, 23 July 2008
Introduction
This is a suggested design of the widgets in the code. The old code is several years old, with very little work done on it.
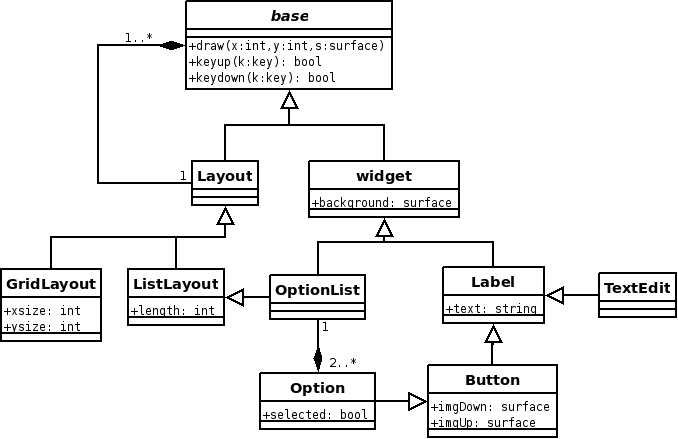
Widgets
Base
This interface defines the draw(), keyup(), and keydown() methods. Every widget will inherit this class. keyup()/keydown() have boolean return types. These methods should return true if they processed the keystroke, and false if they did not.
Widget
A base Widget. This class can have a background image. Any class which will actually draw something to the screen should inherit this class. This class can draw a halo or something similar around itself if it is the active widget.
Label
Can draw a string
TextEdit
Can take input, handles string modification.
Button
A label that can activate a callback. It will contain separate images for each state.
Option
A button that has a state. It should only be instantiated in the context of an OptionList class.
OptionList
A list of options. This class verifies that only one Option object is selected at a time.
Layout
An object of this class can contain other objects. It handles focus and widget traversal by the user. This base class will take coordinates to position its children.
GridLayout
Positions its children in a 2 dimensional grid.
ListLayout
Positions its children in a horizontal or vertically drawn list
Possible Changes
- It may not be necessary for base and widget to be to separate classes. The only reason is if there is a need to differentiate between widget and layout objects.
Screen Shot of Current Work
Beware, programmer art shown:
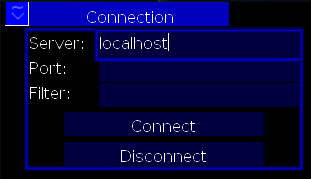 Shown here are two option boxes, three labels, three textboxes, and two buttons. These are contained by a hierarchy of three layout objects.
Shown here are two option boxes, three labels, three textboxes, and two buttons. These are contained by a hierarchy of three layout objects.